Culture Of Pakistan
Identification. As part of India's independence from Great Britain in 1947, a partition took part of their land and created Pakistan as a separate Islamic nation. It is estimated that approximately 95 percent of the population are Muslim, but members of several minority religions live there, including some Hindus, Christians, Parsis, Sikhs, and Buddhists. Although the modern nation of Pakistan was but fifty-three years old in 2000, it has territorial areas and tribal populations whose histories date back many centuries; thus Pakistan has both an ancient and a relatively new identity.
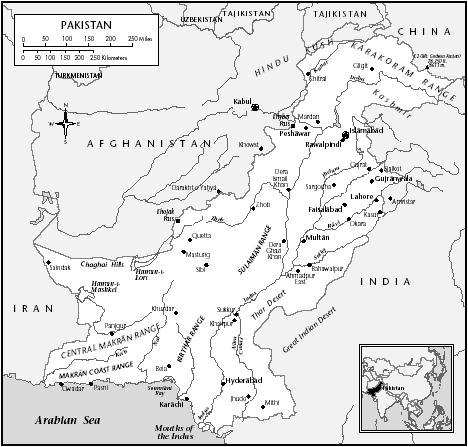
Location and Geography. Pakistan is in South Asia and is 339,697 square miles (879,815 square kilometers) in area. It was created from what had been the northwest side of India. All of the country except the southern portion is landlocked, with Afghanistan to the northwest, Jammu and Kashmir to the northeast, India to the east and southeast, and Iran to the west. In the southern portion, along the shores of the city of Karachi, which was the original capital when the nation was formed in l947, is the Arabian Sea. Karachi is well known for its shorelines. Most of the northern section of the country consists of mountains and also the famous Khyber Pass, whose history goes back several thousand years. It is in this northern section where most of the ancient tribes still live and where many ancient tribal cultures and customs still exist.
Pakistan consists of several provinces, including Punjab, Sind, North-West Frontier, Baluchistan, and the Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA). The city of Islamabad, which is centrally located in the country, was officially named the capital of Pakistan in 1961, and construction began on government buildings in addition to others. Islamabad became the active capital in 1966. In addition to modern government buildings it also features a wide variety of modern hotels, an international airport, and the nearby famous ancient city of Rawalpindi.
In addition to being known for a number of mountains, including K-2, which is the second-highest mountain in world, Pakistan also has several lakes and rivers, including the Indus River, which is 1,800 miles (2,896 kilometers) long. Pakistan also has several deserts, in Punjab and Sind. Pakistan is also home to Taxila, the oldest known university in the world. In the north, leading from China, through Tammu and Kashmir, is a famous ancient silk road. Pakistan is diverse. There are snowcapped mountains in the north, sunny beaches in the south, and a wide variety of geographically and culturally interesting sites elsewhere.
Demography. The population of Pakistan is estimated to be 135 million. An estimated 40 million live in urban areas, with the balance in rural areas. In addition to the residents of the major cities of Islamabad, Karachi, Lahore, and Peshawar, which is the city at the edge of the Kybher Pass gateway, a number of tribal residents live in valleys. These include Chitral Valley, at an elevation of 3,800 feet (1,158 meters), where the majority of the people are Muslims but that also is home to the Kafir-Kalash (wearers of the black robe), a primitive pagan tribe. In Swat Valley, which was once the cradle of Buddhism, Muslim conquerors fought battles and residents claim to be descendants of soldiers of Alexander the Great. In the Hunza Valley, people are noted for longevity, which they claim is because of diet and way of life. The people of Hunza Valley are Muslims and also are believed to be descendants of soldiers of Alexander the Great. In North-West Frontier Province is Kaghan Valley, which is bounded on the west by Swat Valley, on the north by Gilgit, and on the east by Azad Kashmir. The people of Kaghan Valley are Muslim-Pathans as well as Kohistanis and Gujars. Shardu Valley is the capital of the district of Baltistan and is known as "Little Tibet" because the lifestyle there is similar to that in Tibet itself. The people of each of these valley areas are well known for their tribal cultures, handicrafts, and for fascinating clothing, most of which is woven and handmade there and unique to their particular area.
Linguistic Affiliation. The official language of Pakistan is Urdu, but most public officials, people, and others in Pakistan also speak English; English is referred to as the informal official language of Pakistan. Urdu was created by combining the languages of early invaders and settlers, including Arabic, Persian, and Turkish. The spoken form of Urdu is the same as that of Hindi but it is written in a different script than Hindi.
While Urdu and English are prevalent throughout Pakistan, a number of other languages are spoken in different valleys and areas. These include the Punjaki, Sindhi, Pushto, Balochi, Brahvi, Saraiki, and Hindko dialects, among others.
Symbolism. The design of Pakistan's flag was officially adopted by the country's Constituent Assembly in July 1947, it was flown for the first time on their independence day, 14 August l947. The flag was designed by Ali Jinnah, the man acclaimed as the founder of Pakistan. There is a thick white strip on the left side of the flag; the rest of the flag has a dark green background with a white crescent and a five-pointed star centered on it. The white represents peace, and the dark green represents prosperity. The crescent stands for progress, and the star stands for light, guidance, and knowledge. Pakistan also has a national emblem. In the middle of a circled wreath of jasmine flowers is a shield that has four sections, each of which shows a major product of the country from when the country was created. One section shows cotton, another shows wheat, one tea, and one jute. Above the four sections are the crescent and star, as on the national flag. On a scroll beneath the wreath is written in Urdu "Faith, Unity, Discipline."
Location and Geography. Pakistan is in South Asia and is 339,697 square miles (879,815 square kilometers) in area. It was created from what had been the northwest side of India. All of the country except the southern portion is landlocked, with Afghanistan to the northwest, Jammu and Kashmir to the northeast, India to the east and southeast, and Iran to the west. In the southern portion, along the shores of the city of Karachi, which was the original capital when the nation was formed in l947, is the Arabian Sea. Karachi is well known for its shorelines. Most of the northern section of the country consists of mountains and also the famous Khyber Pass, whose history goes back several thousand years. It is in this northern section where most of the ancient tribes still live and where many ancient tribal cultures and customs still exist.
Pakistan consists of several provinces, including Punjab, Sind, North-West Frontier, Baluchistan, and the Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA). The city of Islamabad, which is centrally located in the country, was officially named the capital of Pakistan in 1961, and construction began on government buildings in addition to others. Islamabad became the active capital in 1966. In addition to modern government buildings it also features a wide variety of modern hotels, an international airport, and the nearby famous ancient city of Rawalpindi.
In addition to being known for a number of mountains, including K-2, which is the second-highest mountain in world, Pakistan also has several lakes and rivers, including the Indus River, which is 1,800 miles (2,896 kilometers) long. Pakistan also has several deserts, in Punjab and Sind. Pakistan is also home to Taxila, the oldest known university in the world. In the north, leading from China, through Tammu and Kashmir, is a famous ancient silk road. Pakistan is diverse. There are snowcapped mountains in the north, sunny beaches in the south, and a wide variety of geographically and culturally interesting sites elsewhere.
Demography. The population of Pakistan is estimated to be 135 million. An estimated 40 million live in urban areas, with the balance in rural areas. In addition to the residents of the major cities of Islamabad, Karachi, Lahore, and Peshawar, which is the city at the edge of the Kybher Pass gateway, a number of tribal residents live in valleys. These include Chitral Valley, at an elevation of 3,800 feet (1,158 meters), where the majority of the people are Muslims but that also is home to the Kafir-Kalash (wearers of the black robe), a primitive pagan tribe. In Swat Valley, which was once the cradle of Buddhism, Muslim conquerors fought battles and residents claim to be descendants of soldiers of Alexander the Great. In the Hunza Valley, people are noted for longevity, which they claim is because of diet and way of life. The people of Hunza Valley are Muslims and also are believed to be descendants of soldiers of Alexander the Great. In North-West Frontier Province is Kaghan Valley, which is bounded on the west by Swat Valley, on the north by Gilgit, and on the east by Azad Kashmir. The people of Kaghan Valley are Muslim-Pathans as well as Kohistanis and Gujars. Shardu Valley is the capital of the district of Baltistan and is known as "Little Tibet" because the lifestyle there is similar to that in Tibet itself. The people of each of these valley areas are well known for their tribal cultures, handicrafts, and for fascinating clothing, most of which is woven and handmade there and unique to their particular area.
Linguistic Affiliation. The official language of Pakistan is Urdu, but most public officials, people, and others in Pakistan also speak English; English is referred to as the informal official language of Pakistan. Urdu was created by combining the languages of early invaders and settlers, including Arabic, Persian, and Turkish. The spoken form of Urdu is the same as that of Hindi but it is written in a different script than Hindi.
While Urdu and English are prevalent throughout Pakistan, a number of other languages are spoken in different valleys and areas. These include the Punjaki, Sindhi, Pushto, Balochi, Brahvi, Saraiki, and Hindko dialects, among others.
Symbolism. The design of Pakistan's flag was officially adopted by the country's Constituent Assembly in July 1947, it was flown for the first time on their independence day, 14 August l947. The flag was designed by Ali Jinnah, the man acclaimed as the founder of Pakistan. There is a thick white strip on the left side of the flag; the rest of the flag has a dark green background with a white crescent and a five-pointed star centered on it. The white represents peace, and the dark green represents prosperity. The crescent stands for progress, and the star stands for light, guidance, and knowledge. Pakistan also has a national emblem. In the middle of a circled wreath of jasmine flowers is a shield that has four sections, each of which shows a major product of the country from when the country was created. One section shows cotton, another shows wheat, one tea, and one jute. Above the four sections are the crescent and star, as on the national flag. On a scroll beneath the wreath is written in Urdu "Faith, Unity, Discipline."